Filter
433 results
30
- 10
- 15
- 20
- 25
- 30
- 50
Date, new to old
- Featured
- Best selling
- Alphabetically, A-Z
- Alphabetically, Z-A
- Price, low to high
- Price, high to low
- Date, old to new
- Date, new to old
Sort
Sort by:
- Featured
- Best selling
- Alphabetically, A-Z
- Alphabetically, Z-A
- Price, low to high
- Price, high to low
- Date, old to new
- Date, new to old
-
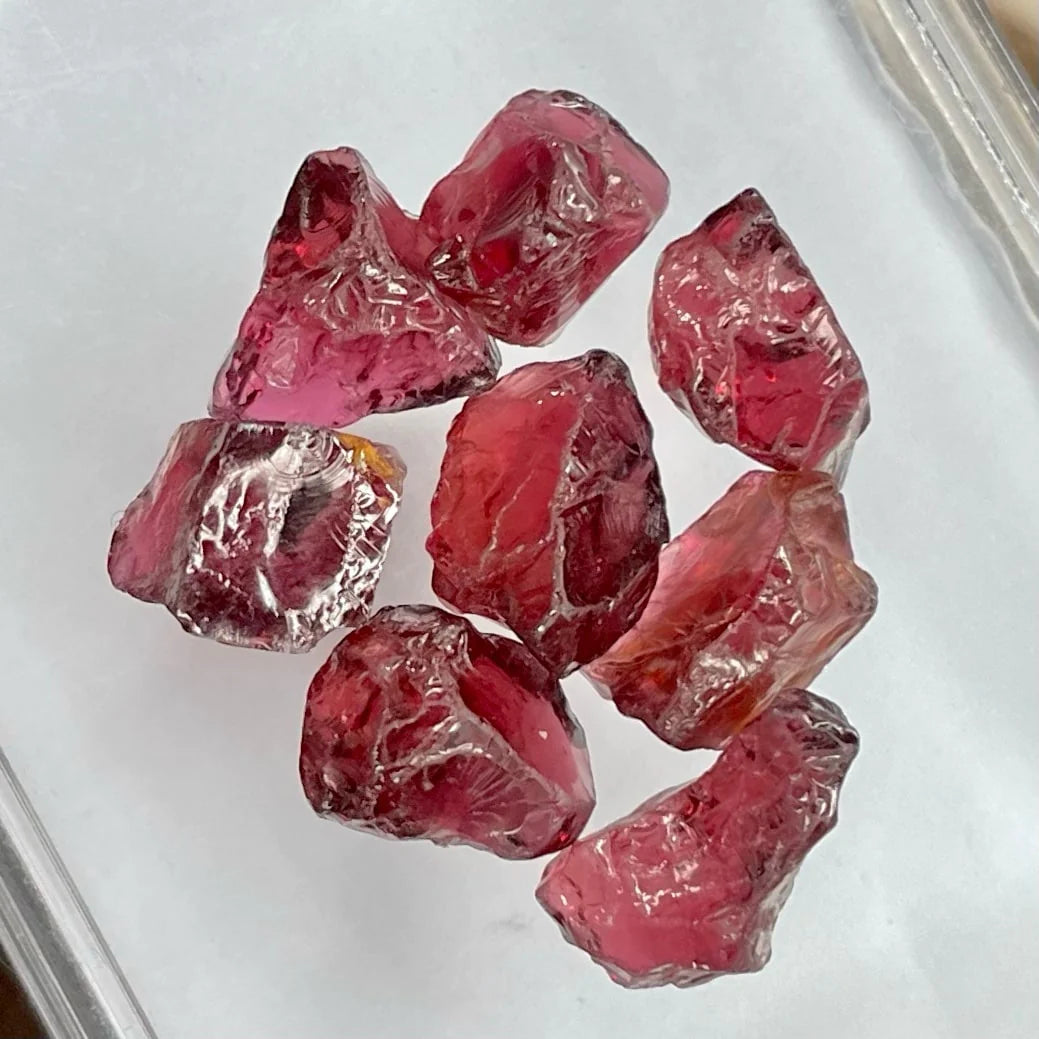
Deep Purplish Red Garnet Facet Rough Parcel
Deep Purplish Red Garnet Facet Rough Parcel Deep Purplish Red Garnet Facet Rough Parcel, available for sale at wholesale price, natural high quality, 65 carats, purplish red rough garnet gemstone from Tanzania. Product Information: Rough Gemstone Deep Purplish Red Garnet Facet Rough Parcel Weight...- $280.00
$286.00- $280.00
- Unit price
- / per
-
Clean Rhodolite Garnet Faceting Rough
Clean Rhodolite Garnet Faceting Rough Clean Rhodolite Garnet Faceting Rough, available for sale at wholesale price, natural high quality, 56.4 carats rough rhodolite garnet gemstone from Tanzania. Product Information: Rough Gemstone Clean Rhodolite Garnet Faceting Rough Weight 56.4 carats Average Weight 8 carats Biggest...- $246.00
- $246.00
- Unit price
- / per
-
Stunning Deep Carmine Garnet Facet Rough Parcel
Stunning Deep Carmine Garnet Facet Rough Parcel Stunning Deep Carmine Garnet Facet Rough Parcel, available for sale at wholesale price, natural high-quality 57.50 carats rough garnet gemstone from Tanzania. Product Information: Rough Gemstone Stunning Deep Carmine Garnet Facet Rough Parcel Weight 57.50 carats Average...- $253.00
- $253.00
- Unit price
- / per
-
Purplish Red Rhodolite Garnet Facet Rough
Purplish Red Rhodolite Garnet Facet Rough Purplish Red Rhodolite Garnet Facet Rough, available for sale at wholesale price, natural high-quality, 56 carats rough Rhodolite garnet gemstone from Tanzania. Product Information: Rough Gemstone Purplish Red Rhodolite Garnet Facet Rough Weight 56 carats Average Weight 8...- $246.00
- $246.00
- Unit price
- / per
-
Deep Carmine Garnet Facet Rough Parcel
Deep Carmine Garnet Facet Rough Parcel Deep Carmine Garnet Facet Rough Parcel, available for sale at wholesale price, natural high-quality, 70.50 carats rough garnet gemstone from Tanzania. Product Information: Rough Gemstone Deep Carmine Garnet Facet Rough Parcel Weight 70.50 carats Average Weight 7.83 carats...- $310.00
- $310.00
- Unit price
- / per
-
Milano Red Rhodolite Garnet Facet Rough
Milano Red Rhodolite Garnet Facet Rough Milano Red Rhodolite Garnet Facet Rough, available for sale at wholesale price, natural high-quality rough garnet gemstone from Tanzania. Product Information: Rough Gemstone Milano Red Rhodolite Garnet Facet Rough Weight 63.75 carats Average Weight 7.96 carats Biggest Piece...- $280.00
- $280.00
- Unit price
- / per
-
Facet Rough Brown Topaz Pieces
Facet Rough Brown Topaz Pieces Facet Rough Brown Topaz Pieces, available for sale, natural high-quality rough gemstones, eye clean, 197.20 carats rough topaz from Madagascar. Product Information: Gemstone Type Facet Rough Brown Topaz Pieces Weight 197.20 carats Average Weight 65.74 carats Clarity SI to...- $145.00
- $145.00
- Unit price
- / per
-
Light Brown Topaz Facet Rough Parcel
Light Brown Topaz Facet Rough Parcel Light Brown Topaz Facet Rough Parcel, available for sale, natural high-quality rough gemstones, eye clean, 306 carats rough topaz from Madagascar. Product Information: Gemstone Type Light Brown Topaz Facet Rough Parcel Weight 306 carats Average Weight 25.5 carats...- $225.00
- $225.00
- Unit price
- / per
-
Facet Rough Light Brown Topaz Parcel
Facet Rough Light Brown Topaz Parcel Facet Rough Light Brown Topaz Parcel, available for sale, natural high-quality rough gemstones, eye clean, 166 carats rough topaz from Madagascar. Product Information: Gemstone Type Facet Rough Light Brown Topaz Parcel Weight 166 carats Average Weight 16.6 carats...- $120.00
$145.00- $120.00
- Unit price
- / per
-
Light Blue Topaz Facet Rough Parcel
Light Blue Topaz Facet Rough Parcel Light Blue Topaz Facet Rough Parcel, available for sale at wholesale price, natural high-quality rough gemstones, eye clean, 193.85 carats rough topaz from Madagascar. Product Information: Gemstone Type Light Blue Topaz Facet Rough Parcel Weight 193.85 carats Average...- $140.00
$155.00- $140.00
- Unit price
- / per
-
200.50 Carats Facet Rough Light Blue Topaz
Facet Rough Light Blue Topaz, available for sale, natural high-quality rough gemstones, eye clean, 200.50 carats rough topaz from Madagascar. Product Information: Gemstone Type Facet Rough Light Blue Topaz Weight 200.50 carats Average Weight 25 carats Clarity SI to Eye Clean Origin Madagascar Treatment...- $145.00
- $145.00
- Unit price
- / per
-
6.05 Carats Orange Brown Mali Garnet Facet Rough
Orange Brown Mali Garnet Facet Rough, available for sale at wholesale price, natural high-quality rough gemstone, garnet facet rough from Mali. Product Information: Rough Gemstone Orange Brown Mali Garnet Facet Rough Weight 6.05 carats Dimensions 11 x 8 x 7.8 mm Clarity VVS Origin...- $90.00
- $90.00
- Unit price
- / per
-
Preformed Bolivianite Facet Rough Trio
Preformed Bolivianite Facet Rough Trio, available for sale at wholesale price, natural high-quality, preformed bolivianite gemstones trio from Bolivia. Product Information: Rough Gemstone Preformed Bolivianite Facet Rough Trio Weight 78.25 carats Average Weight 26.03 carats Biggest Piece 27.90 carats Smallest Piece 24.35 carats No....- $140.00
$155.00- $140.00
- Unit price
- / per
-
Facet Rough Neon Blue Apatite Lot
Neon Blue Apatite Facet Rough Parcel, available for sale at wholesale price, natural high-quality rough gemstone, eye clean, rough apatite from Brazil. Product Information: Rough Gemstone Facet Rough Neon Blue Apatite Lot Weight 55 carats Average Weight 3.05 carats Biggest Piece 4 carats Smallest...- $110.00
- $110.00
- Unit price
- / per
-
5.05 Carats Facet Rough Grossular Mali Garnet
Facet Rough Grossular Mali Garnet, available for sale at wholesale price, natural high-quality rough gemstone, eye clean, rough grossular garnet from Mali. Product Information: Rough Gemstone Facet Rough Grossular Mali Garnet Weight 5.05 carats Dimensions 9 x 8 x 7.5 mm Clarity Eye Clean...- $105.00
- $105.00
- Unit price
- / per
-
5.85 Carats Mali Garnet Facet Rough
Mali Garnet Facet Rough, available for sale at wholesale price, natural high-quality rough gemstone, eye clean, rough garnet from Mali. Product Information: Rough Gemstone Mali Garnet Facet Rough Weight 5.85 carats Dimensions 11 x 8 x 8 mm Clarity Eye Clean Origin Mali Treatment...- $120.00
- $120.00
- Unit price
- / per
-
79 Carats Facet Grade Rough Fluorite Lot
79 Carats Facet Grade Rough Fluorite Lot, available for sale at wholesale price, natural high-quality, eye to loupe clean clarity, rough fluorite from Madagascar. Product Information: Rough Gemstone Facet Grade Rough Fluorite Lot Weight 79 carats Average Size 13.16 carats Biggest Piece 18.60 carats...- $115.00
- $115.00
- Unit price
- / per
-
85 Carats Preformed Ametrine Facet Rough Gemstone
Preformed Ametrine Facet Rough Gemstone, available for sale at wholesale price, natural high-quality 85 carats rough ametrine gemstones from Bolivia. Product Information: Rough Gemstone Preformed Ametrine Facet Rough Gemstone Weight 85 carats Average Weight 28.33 carats Biggest Piece 33.55 carats Smallest Piece 25 carats...- $155.00
- $155.00
- Unit price
- / per
-
6.25 carats Orange Grossular Garnet Facet Rough
Orange Grossular Garnet Facet Rough, available for sale, natural high-quality rough gemstone, eye clean, 6.25 carats rough garnet from Mali. Product Information: Rough Gemstone Orange Grossular Garnet Facet Rough Weight 6.25 carats Dimensions 11 x 8 x 7 mm Clarity Eye Clean Origin Mali...- $125.00
- $125.00
- Unit price
- / per
-
59 carats Greenish Yellow Peridot Facet Rough Parcel
59 carats Greenish Yellow Peridot Facet Rough Parcel, available for sale, natural high-quality, slightly included to eye clean, rough peridot from Pakistan. Product Information: Gemstone Name Greenish Yellow Peridot Facet Rough Parcel Weight 59 carats Average Weight 4.53 carats Biggest Piece 6.40 carats Smallest...- $175.00
- $175.00
- Unit price
- / per
-
Facet Rough Neon Blue Apatite Parcel
Facet Rough Neon Blue Apatite Parcel, available for sale at wholesale price, natural high-quality 50 carats rough apatite from Brazil. Product Information: Rough Gemstone Facet Rough Neon Blue Apatite Parcel Weight 50 carats Average Weight 3. 125 carats Biggest Piece 3.50 carats Smallest Piece...- $100.00
- $100.00
- Unit price
- / per
-
71.55 Carats Beautiful Fluorite Facet Rough Lot
71.55 Carats Beautiful Fluorite Facet Rough Lot, available for sale, natural high-quality, eye to loupe clean clarity, 71.55 carats rough fluorite from Madagascar. Product Information: Rough Gemstone Beautiful Fluorite Facet Rough Lot Weight 71.55 carats Average Size 7.15 carats Biggest Piece 12.75 carats Smallest...- $105.00
- $105.00
- Unit price
- / per
-
78 Carats Facet Rough Preformed Ametrine Pieces
78 Carats Facet Rough Preformed Ametrine Pieces, available for sale at wholesale price, natural high-quality 78 carats rough ametrine gemstones from Bolivia. Product Information: Rough Gemstone Facet Rough Preformed Ametrine Pieces Weight 78 carats Average Weight 26 carats Biggest Piece 26.65 carats Smallest Piece...- $140.00
$145.00- $140.00
- Unit price
- / per
-
79.40 carats Facet Rough Preformed Ametrine Trio
79.40 carats Facet Rough Preformed Ametrine Trio, available for sale at wholesale price, natural high-quality rough ametrine gemstones from Bolivia. Product Information: Rough Gemstone Facet Rough Preformed Ametrine Trio Weight 79.40 carats Average Weight 26.46 carats Biggest Piece 28.50 carats Smallest Piece 23.35 carats...- $145.00
- $145.00
- Unit price
- / per
-
6.15 carats Grossular Mali Garnet Facet Rough
6.15 Grossular Mali Garnet Facet Rough, available for sale, natural high-quality rough gemstone, 6.15 carats rough garnet from Mali. Product Information: Rough Gemstone Grossular Mali Garnet Facet Rough Weight 6.15 carats Dimensions 10 x 8 x 7 mm Clarity Eye Clean Origin Mali Treatment...- $125.00
- $125.00
- Unit price
- / per
-
85.85 Carats Preformed Ametrine Trio Facet Rough
85.85 Carats Preformed Ametrine Trio Facet Rough, available for sale at wholesale price, natural high-quality rough ametrine gemstones from Bolivia. Product Information: Rough Gemstone Preformed Ametrine Trio Facet Rough Weight 85.85 carats Average Weight 28.61 carats Biggest Piece 34.30 carats Smallest Piece 24.95 carats...- $155.00
- $155.00
- Unit price
- / per
-
68.40 Carats Preformed Ametrine Duo Facet Rough
68.40 Carats Preformed Ametrine Duo Facet Rough, available for sale, natural high-quality rough gemstone, ametrine gemstone duo from Bolivia. Product Information: Rough Gemstone Preformed Ametrine Duo Facet Rough Weight 68.40 carats Average Weight 34.2 carats Biggest Piece 35.05 carats Smallest Piece 33.35 carats No....- $125.00
- $125.00
- Unit price
- / per
-
85.70 carats Preformed Ametrine Facet Rough Trio
85.70 carats Preformed Ametrine Facet Rough Trio, available for sale at wholesale price, natural high-quality rough ametrine gemstone from Bolivia. Product Information: Rough Gemstone Preformed Ametrine Facet Rough Trio Weight 85.70 carats Average Weight 28.56 carats Biggest Piece 30.60 carats Smallest Piece 26.20 carats...- $155.00
$160.00- $155.00
- Unit price
- / per
-
88.6 Carats Facet Rough Pistachio Green Peridot Lot
88.6 Carats Facet Rough Pistachio Green Peridot Lot, available for sale, natural high-quality, eye clean, rough peridot gemstone from Pakistan. Product Information: Gemstone Name Facet Rough Pistachio Green Peridot Lot Weight 88.6 carats Average Weight 4.02 carats Biggest Piece 7 carats Smallest Piece 3...- $175.00
- $175.00
- Unit price
- / per
-
77 Carats Madagascar Scapolite Facet Rough Pieces
77 Carats Madagascar Scapolite Facet Rough Pieces, available for sale, natural high-quality loupe clean, rough scapolite gemstone from Ihosy. Product Information: Gemstone Type Madagascar Scapolite Facet Rough Pieces Weight 77 carats Average Weight 19.25 carats Biggest Piece 29.30 carats Smallest Piece 8.40 carats No....- $77.00
- $77.00
- Unit price
- / per